What does the market want?
Demand for Housing Choice
A greater variety of household sizes and demographics require a greater variety of housing choices.
Young, highly educated, technology-driven millennials desire mobile, walkable lifestyles. They are willing to exchange space for shorter commutes, mixed-use neighborhoods, and shared open spaces that foster community interaction.
At the same time, baby boomers are working and living longer. They want to stay mobile and active in their later years, but they won’t drive forever and don’t want to be dependent on their family members to get around. They also want to find ways to stay in their community without having to care for a large home and yard.
Multigenerational homes have increased by 17% since 1940, and that number continues to rise. The growing senior population, more families with multiple working parents, diverse family cultures, and an increased desire to live in intergenerational neighborhoods all contribute to the growing demand for multigenerational and even multi-family households. Affluent seniors seek to downsize from their large suburban homes to more convenient, easy-to-care-for townhouses, apartments, or condos, while others need quality, affordable housing that won’t break their limited budget. Many retirees would like to move close to, but not live with, their children and grandchildren.
The growing demand for a walkable lifestyle has the potential to transform sprawling suburbs into walkable communities.
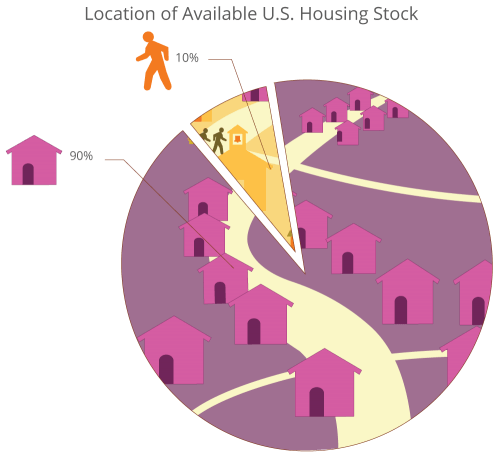
90% of available housing in the U.S. is located in a conventional neighborhood of single-family homes, adding up to a 35 million unit housing shortage. Source: Dr. Arthur C. Nelson, “Missing Middle: Demand and Benefits,” Utah Land Use Institute conference, October 21, 2014.
Walkable and Accessible Amenities
Up to 85% of households will be childless by 2025.
“This country is in the middle of a structural shift toward a walkable urban way of living. After 60 years of almost exclusively building a drivable suburban way of life … the consumer is now demanding the other alternative,” wrote Christopher Leinberger in the New York Times article “Car-Free in America? Bottom Line: It’s Cheaper.”
By 2020, 34% of all American households will consist of a single person, and many of these will be women, or older persons. By 2025, up to 85% of households will be childless as millennials choose to marry later and have fewer children and the number of empty nester households continues to grow.
Housing trends show singles demand more amenities, and women and older persons who live alone generally seek housing options that offer better security. They also drive less, reducing the need for off-street parking in private garages or lots, and increasing the need for accessible public transportation.
“The present economic research finds that business wants talent, but talent wants place—so more businesses are relocating to places. When drilled further the research finds Missing Middle Housing is the fastest growing preference because it has the ‘place’ quality talent seeks. Hence development of Missing Middle is now recognized as a housing AND economic development strategy.”
— James Tischler, Michigan State Housing Development Authority
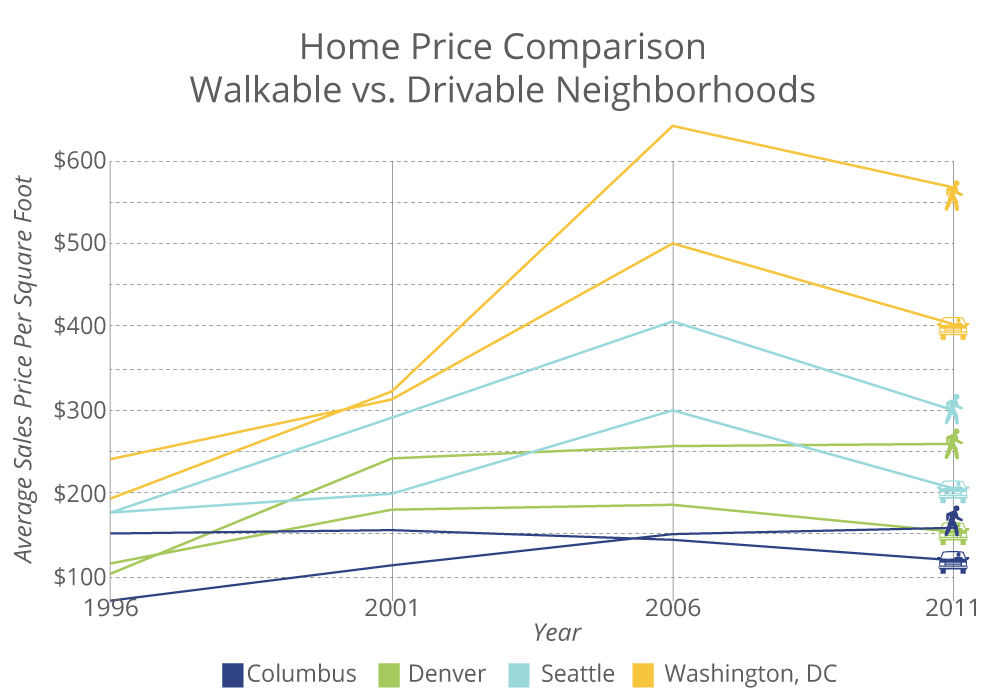
According to the National Association of Realtors, walkability is fast becoming one of the most important factors in choosing where to live. People want of all ages want easy access to amenities such as stores, businesses, cultural center, and transit.Homebuyers are seeking locations within walking distance to shopping, cultural amenities, jobs, and open space and the value of homes in these types of neighborhoods has increased at a much faster pace than homes in driveable suburban neighborhoods. “In a scenario where two houses are nearly identical, the one with a five-foot-wide sidewalk and two street tress not only sells for up to $34,000 more, but it also sells in less time,” wrote J. Cortright, in CEOs for Cities’ Walking the Walk: How Walkability Raises Home Values in U.S. Cities. But, as the chart at the right shows, now you don’t have to live in a dense urban center to live a walkable lifestyle. Some 70% of upcoming, walkable places in Washington D.C. are quaint neighborhoods located outside of the urban core.
Variety of Transportation
Accessibility to useful multimodal transit—public transportation, bike friendly streets, and car share—is needed by baby boomers and desired by millennials. But there is an economic argument, too.
“American families who are car-dependent spent 25% of their household income on their fleet of cars, compared to just 9% for transportation for those who live in walkable urban places,” says Leinberger.
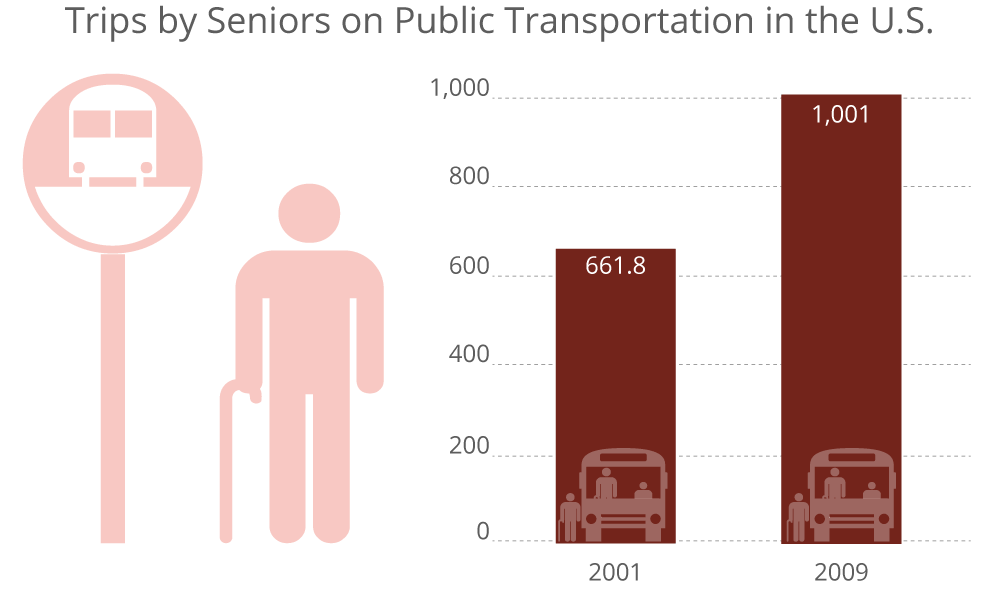
Walkable neighborhoods are now a top priority for seniors, along with access to transportation, and connectivity. Source: What’s Next? Real Estate in the New Economy, Urban Land Institute, 2011; Transportation for America.
The same is true for bike friendly cities. According to the Livable Street Alliance, as reported on the AARP Livability Fact Sheet, the average American household spends more than $8,000 a year on cars while the cost to maintain a bicycle is only about $300 per year. These savings, which could amount into the billions if trends were widely adopted, could be reinvested into transit-oriented development and infrastructure, education, and health care.
Cities and property owners benefit from less car dependent zoning too. “An off-street parking space costs between $3,000 and $27,000 to build, and about $500 a year to maintain and manage. On-street parking is more efficient and can bring in as much as $300,000 per space in annual revenues,” writes Prof. Donald Shoup, in Instead of Free Parking.
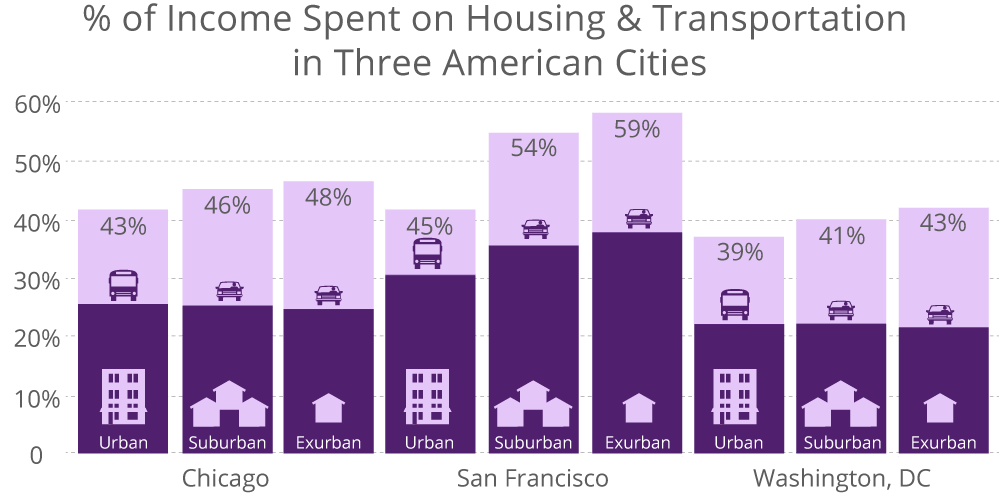
An increasing number of Americans spend close to 30% of their income on housing while transportation costs can consume an additional 20% or more of household income. Source: What’s Next? Real Estate in the New Economy, Urban Land Institute, 2011.
Affordability
Housing affordability is a primary concern for many Americans across the country ranging from blue-collar workers to early-career singles, young families and seniors. There is an increasing segment of the population that spends more than 30% of their income on housing, reducing their purchasing power for other amenities (Source: What’s Next? Real Estate in the New Economy, Urban Land Institute, 2011).
Smaller homes and apartments cost less to rent or purchase and maintain, while urban neighborhoods provide services and amenities within walking distance as well as a variety of affordable transportation options.
Cities and towns that want to retain or attract these household types need to focus on providing diverse, affordable housing options near jobs, schools, and other amenities within walkable communities. In addition, suburbs that want to retain their aging populations and attract newer, younger families, will need to create new, walkable urban environments and encourage the construction fo Missing Middle Housing through rezoning and by providing public transportation options.
Sense of Community
More and more, Americans say living in a diverse community that includes people at all stages of life is an important factor in determining where to live.
Seniors want to live near family and friends, but not with them. Missing Middle building types allow people to stay in their community thoroughout their lives because of the variety of sizes available and an increased accessibility to services and amenities.
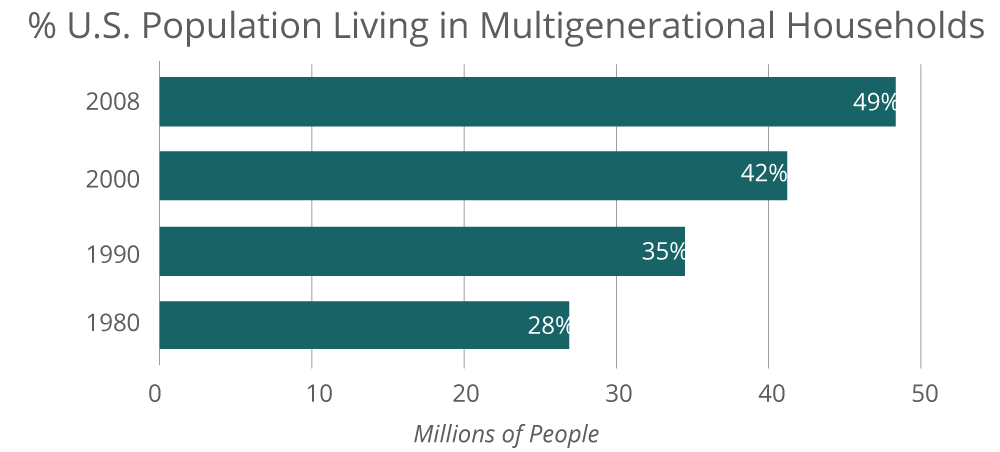
Almost 49% of Americans are living in a multigenerational household. Source: Pew Research Center analysis of U.S. Decennial Census and American Community Surveys.
According to Chris Leinberger in his article “The Next Slum?” for The Atlantic, elements that used to draw families into the suburbs—better schools and safer communities—are now becoming the norm in cities, while these elements could worsen in suburbs that are dependent on home values and new development.
Housing market projections suggest that construction in the near future will accelerate only moderately for single-family housing but will greatly increase for multifamily housing (Source: Jordan Rappaport, “The Demographic Shift From Single-Family to Multifamily Housing,” Economic Review, Kansas City: Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City, 2013). Implemented in both urban and rural contexts, Missing Middle Housing allows people to stay in their community during different stages of life because of the wide variety of sizes, housing levels, and accessibility it provides.